Using Website Event Tagging Data to A/B Test Ads
Hypothesis: There is a difference in purchases as a result of the new ad.
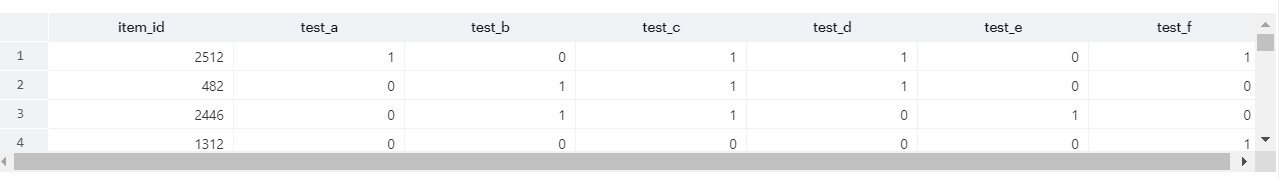
Check the table
We are running an experiment at an item-level, which means all users who visit will see the same page, but the layout of different item pages may differ. Compare this table to the assignment events we captured for user_level_testing. Does this table have everything you need to compute metrics like 30-day view-binary?
SELECT
*
FROM
dsv1069.final_assignments_qa
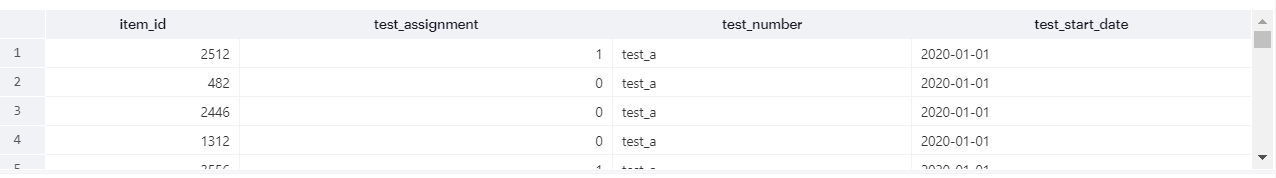
Reformat the table
Reformat the final_assignments_qa to look like the final_assignments table, filling in any missing values with a placeholder of the appropriate data type.
SELECT
item_id,
test_a AS test_assignment,
'test_a' AS test_number,
'2020-01-01' AS test_start_date
FROM
dsv1069.final_assignments_qa
Order Binary Metric
Create order binary for test.
SELECT
test_assignment,
COUNT(item_id) as items,
SUM(order_binary_30d) AS items_ordered_30d
FROM
(
SELECT
f.test_assignment,
f.item_id,
MAX(CASE WHEN orders.created_at > f.test_start_date THEN 1 ELSE 0 END) AS order_binary_30d
FROM
dsv1069.final_assignments f
LEFT OUTER JOIN
dsv1069.orders
ON
f.item_id = orders.item_id
AND
orders.created_at >= f.test_start_date
AND
DATE_PART('day', orders.created_at - f.test_start_date ) <= 30
WHERE
f.test_number= 'item_test_2'
GROUP BY
f.test_assignment,
f.item_id
) item_orders
GROUP BY test_assignment

View Item Metric
Compute view item metrics.
SELECT
test_assignment,
COUNT(item_id) AS items,
SUM(view_binary_30d) AS viewed_items,
CAST(100*SUM(view_binary_30d)/COUNT(item_id) AS FLOAT) AS viewed_percent,
SUM(views) AS views,
SUM(views)/COUNT(item_id) AS average_views_per_item
FROM
(
SELECT
f.test_assignment,
f.item_id,
MAX(CASE WHEN item_views.event_time > f.test_start_date THEN 1 ELSE 0 END) AS view_binary_30d,
COUNT(item_views.event_id) AS views
FROM
dsv1069.final_assignments f
LEFT OUTER JOIN
(
SELECT
event_time,
event_id,
CAST(parameter_value AS INT) AS item_id
FROM
dsv1069.events
WHERE
event_name = 'view_item'
AND
parameter_name = 'item_id'
) item_views
ON
f.item_id = item_views.item_id
AND
item_views.event_time >= f.test_start_date
AND
DATE_PART('day', item_views.event_time - f.test_start_date ) <= 30
WHERE
f.test_number= 'item_test_2'
GROUP BY
f.test_assignment,
f.item_id
) item_orders
GROUP BY
test_assignment

Results

Using the A/B testing required from this link: https://thumbtack.github.io/abba/demo/abba.html, I was able to calculate the p-value for a 95% confidence interval. There was an improvement of 2.6% in the conversion rate of products with the new ad. However, with a p value of .2 the results are not statistically significant. Therefore, we cannot conclude that the variation in conversion rate was caused by the new ad.