Scraping AWS Pricing Data
The sales team at my workplace needed AWS EC2 Instance Pricing which gets updated regularly. However, every time it is updated, they have to manually update the entire document which is a time-intensive process that takes weeks. I was able to automate this process to get the most up-to-date and only the most pertinent results for them in a CSV file.
Understanding the data
First, I imported the libraries I needed to work with.
import pandas as pd
import requests
import io
Then I needed to open the AWS Region Index from a URL which was in JSON format.
aws_url = "https://pricing.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/offers/v1.0/aws/AmazonEC2/current/region_index.json"
r = requests.get(aws_url, allow_redirects=True)
data = r.json()
Extracting values of keys from nested JSON
Seeing as the region and URL values I was looking for were nested, I used a function to extract values from any key I needed.
def json_extract(obj, key):
# Recursively fetch values from nested JSON.
arr = []
def extract(obj, arr, key):
# Recursively search for values of key in JSON tree.
if isinstance(obj, dict):
for k, v in obj.items():
if isinstance(v, (dict, list)):
extract(v, arr, key)
elif k == key:
arr.append(v)
elif isinstance(obj, list):
for item in obj:
extract(item, arr, key)
return arr
values = extract(obj, arr, key)
return values
Then I extracted the Region Names and Region URL Extensions to a list, and then a dictionary for the ability to easily sub-query specific regions in the future.
# Extract Region Names to list
regions = json_extract(data, 'regionCode')

# Extract Region URL Extensions to list
region_url = json_extract(data, 'currentVersionUrl')
# Create a dictionary of paired Region Names and URL Extensions
region_dict = {'Region':regions, 'URL': region_url}
Amazon allows you to use a CSV or JSON file, and since I wanted to use the CSV file for easier querying I replaced ‘json’ with ‘csv’ so downloaded files are CSV format.
region_url_csv = [url.replace('json', 'csv') for url in region_url]
Creating the pricing list
Now, I had to set up a dataframe to add the data I wanted. The base_url is used in every URL, so the unique URL extensions will be added to it to form the full URL.
# Create column list (you can add/remove columns you want)
column_list = ['SKU', 'OfferTermCode', 'RateCode', 'TermType', 'PriceDescription', 'EffectiveDate', 'Unit', 'PricePerUnit', 'Currency', 'LeaseContractLength', 'PurchaseOption', 'OfferingClass', 'Product Family', 'serviceCode', 'Location', 'Location Type', 'Instance Type', 'Current Generation', 'Instance Family', 'vCPU', 'Memory', 'Tenancy', 'Operating System', 'Pre Installed S/W']
# Create blank dataframe with columns from column_list
pricing_list = pd.DataFrame(columns=column_list)
# The base url used for every complete URL
base_url = 'https://pricing.us-east-1.amazonaws.com'
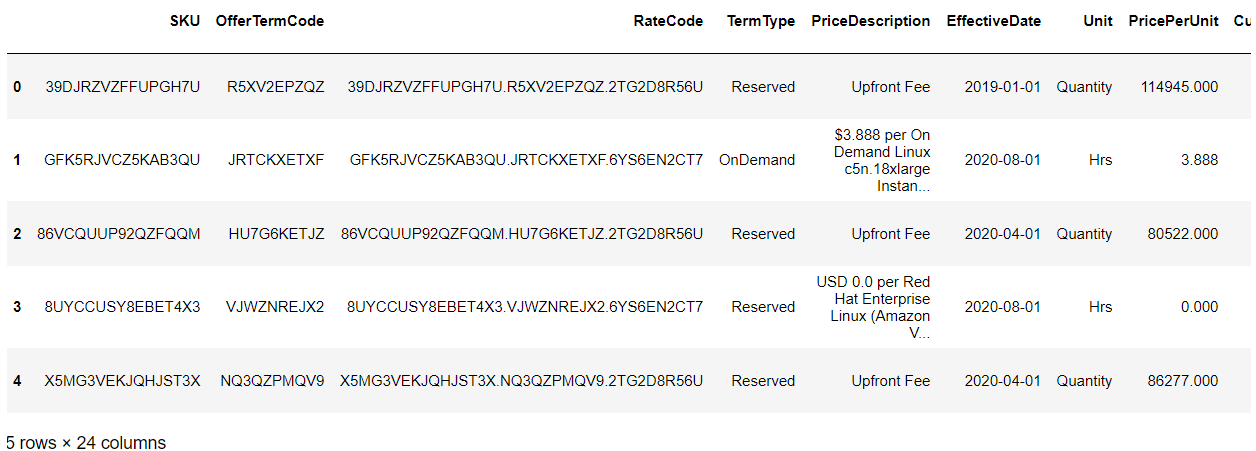
At this point I created a loop that will add each CSV file from the URL list to the pricing_list dataframe.
for url in region_url_csv:
# Get csv data from URL
r = requests.get(base_url+url).content
# Read CSV data to dataframe
region_price = pd.read_csv(io.StringIO(r.decode("utf-8")), skiprows=5, usecols=column_list)
# Append data to pricing_list dataframe
pricing_list = pricing_list.append(region_price, ignore_index=True)
Then, I took our 3 subsets of the dataframe and merged them together to make a smaller file.
# Create dataframes from substet of pricing_list dataframe for each pricing type (you can adjust parameters)
on_demand = pricing_list[pricing_list['TermType']=='OnDemand']
one_yr_no_upfront = pricing_list[(pricing_list['TermType']=='Reserved') & (pricing_list['LeaseContractLength']=='1yr') & (pricing_list['PurchaseOption']=='No Upfront') & (pricing_list['OfferingClass']=='standard')]
three_yr_conv = pricing_list[(pricing_list['TermType']=='Reserved') & (pricing_list['LeaseContractLength']=='3yr') & (pricing_list['PurchaseOption']=='No Upfront') & (pricing_list['OfferingClass']=='convertible')]
# Create final_pricing dataframe by appending the pricing types dataframes
final_pricing = on_demand.append(one_yr_no_upfront.append(three_yr_conv, ignore_index=True), ignore_index=True)
Lastly, I created and compressed the CSV file into a zip folder.
# Name file and compression type
compression_opts = dict(method='zip',
archive_name='AWSEC2Pricing.csv')
# Convert data to CSV and compress to zip file
final_pricing.to_csv('awsec2pricing.zip', index=False,
compression=compression_opts)